Project 2.20: Efficiency of Fiber Reinforcement in Ultra-high Performance Concrete
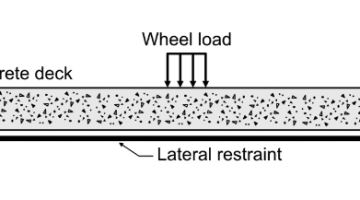
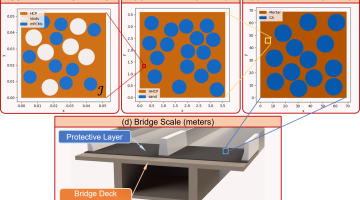
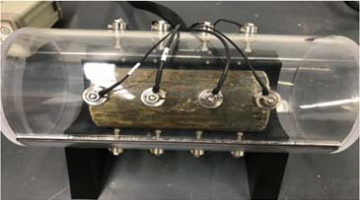
Efficiency of Fiber Reinforcement in Ultra-high Performance Concrete Project 2.20 Project Summary The proposed research aims at investigating the efficiency of fiber reinforcement in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) mixtures. This proposed research is a necessary step for the successful completion of the development of non-proprietary UHPC mixtures. Since fiber reinforcement is the most expensive part […]
Read more